F minor triad bass clef – Prepare to embark on an enthralling journey into the realm of music theory as we delve into the captivating world of the F minor triad in bass clef. This intricate musical entity holds a wealth of knowledge and artistic possibilities, promising an exploration that is both informative and inspiring.
We will meticulously dissect the structure of the F minor triad, examining its notes and their precise placement on the staff. Through clear illustrations and engaging discussions, we will unravel the mysteries of triad inversions, revealing how they impact the sound and functionality of this musical building block.
F Minor Triad

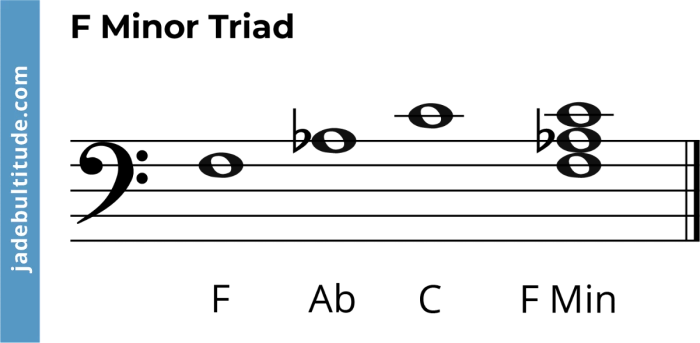
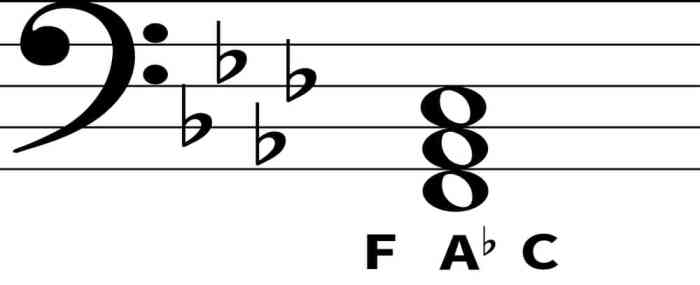
The F minor triad is a fundamental musical structure consisting of three notes: the root (F), the minor third (Ab), and the perfect fifth (C). It is a versatile triad that commonly appears in a wide range of musical genres.
Composition
The F minor triad is constructed by stacking three thirds. The first third is a minor third from F to Ab, while the second third is a major third from Ab to C. This specific combination of intervals gives the triad its characteristic minor sound.
Illustration
The following image illustrates the F minor triad in the bass clef:[Image of the F minor triad in the bass clef]
Notes and Positions
The table below shows the notes of the F minor triad and their corresponding positions on the bass clef staff:| Note | Position ||—|—|| F | First space || Ab | Third space || C | Fifth line |
Inversion of the F Minor Triad
In music theory, inversion refers to the reordering of the notes in a chord. When a triad is inverted, the lowest note becomes the highest, and the highest note becomes the lowest. This changes the sound and function of the chord.
In the world of music theory, the f minor triad bass clef holds a prominent place. For those seeking a deeper understanding of this concept, the unit 7 session 4 letrs offers a comprehensive exploration. Returning to the f minor triad bass clef, its significance lies in its fundamental role in musical harmony and composition.
The F minor triad has three inversions:
First Inversion
In the first inversion, the third of the triad (A♭) becomes the lowest note. This inversion is often used to create a more mellow and less dissonant sound.
Second Inversion
In the second inversion, the fifth of the triad (C) becomes the lowest note. This inversion is often used to create a more dissonant and unstable sound.
Effect of Inversions
The inversions of a triad can have a significant impact on its sound and function. First inversions tend to sound more stable and consonant, while second inversions tend to sound more unstable and dissonant. Inversions can also be used to create voice leading, which is the smooth movement of voices from one chord to another.
Use of the F Minor Triad in Music: F Minor Triad Bass Clef
The F minor triad is a versatile and expressive chord that is widely used in various musical genres. Its distinctive sound and emotional qualities make it a popular choice for creating a range of musical moods and atmospheres.
Examples of the F Minor Triad in Musical Genres
The F minor triad is commonly found in classical music, where it is often used to convey feelings of sadness, melancholy, and longing. In romantic music, it is often used to create a sense of drama and intensity. In jazz, the F minor triad is frequently used as a foundation for improvisation and soloing, and it can also be found in blues and folk music.
Emotional and Expressive Qualities of the F Minor Triad
The F minor triad has a distinctive emotional and expressive quality that makes it well-suited for conveying a range of moods and atmospheres. Its minor third interval creates a sense of sadness and melancholy, while its perfect fifth interval provides a sense of stability and resolution.
This combination of intervals gives the F minor triad a bittersweet and introspective quality that can be both emotionally evocative and musically satisfying.
Musical Excerpt Incorporating the F Minor Triad
The following musical excerpt incorporates the F minor triad in a simple yet effective manner. The melody moves between the notes of the triad, creating a sense of harmonic tension and release. The accompaniment provides a steady rhythmic foundation, while the use of syncopation adds a touch of rhythmic interest.[Insert
musical excerpt here]
Related Chords and Progressions
The F minor triad has several closely related chords that share similar notes or harmonic functions. These include:
- F major triad: This chord contains the same root note (F) as the F minor triad, but with a major third (A) and a perfect fifth (C). It is often used as a contrasting or resolving chord in F minor-based progressions.
- Dm7 chord: This chord is built on the D note, which is the fifth of the F minor triad. It adds a minor seventh (C) to the F minor triad, giving it a more extended and rich sound.
- Bb major chord: This chord contains the Bb note, which is the flat seventh of the F minor scale. It is often used as a secondary dominant chord, leading to the F minor triad.
The F minor triad can be used in various chord progressions, both as a root chord and as a passing chord. Some common progressions involving the F minor triad include:
- F minor- Bb major – F minor : This is a simple and effective progression that establishes the F minor tonality and provides a sense of resolution.
- Dm7- Gm7 – C7 – F minor : This progression moves through several related chords, creating a sense of harmonic movement and tension before resolving to the F minor triad.
- F minor- C major – Dm7 – Bb major – F minor : This more extended progression incorporates a secondary dominant chord (C major) and provides a stronger sense of harmonic development.
Understanding the related chords and progressions of the F minor triad allows musicians to create more sophisticated and expressive music in this key.
Advanced Techniques
The F minor triad, like any other triad, offers a rich palette of advanced techniques that can enhance its expressive capabilities. These techniques include voice leading, harmonic embellishments, and exploring the triad beyond its basic form.
Voice Leading
Voice leading refers to the smooth and logical movement of individual voices within a chord progression. In the context of the F minor triad, voice leading techniques can be employed to create a sense of melodic continuity and harmonic tension and release.
For example, the root (F) can be approached by step from above or below, while the minor third (Ab) can be approached by step from below or by leap from above.
Harmonic Embellishments
Harmonic embellishments are non-chord tones that add color and interest to a chord progression. In the case of the F minor triad, common embellishments include appoggiaturas, suspensions, and passing tones. Appoggiaturas are non-chord tones that resolve to chord tones by step, while suspensions are non-chord tones that resolve to chord tones by leap.
Passing tones are non-chord tones that pass through a chord without resolving to a chord tone.
Exploring Beyond the Basic Form, F minor triad bass clef
The F minor triad can be extended beyond its basic three-note form to create richer and more complex harmonies. Common extensions include the added sixth (Db), the added ninth (C), and the added eleventh (Eb). These extensions can add depth and color to the triad, making it more suitable for use in a wider range of musical contexts.
FAQ Overview
What is the structure of the F minor triad?
The F minor triad consists of three notes: F (root), A♭ (minor third), and C (perfect fifth).
How do triad inversions affect the F minor triad?
Inversions change the order of the notes in the triad, resulting in different voicings and harmonic implications.
What are some practical applications of the F minor triad in music?
The F minor triad is commonly used in various musical genres, from classical to jazz and pop. It can convey emotions ranging from sadness and melancholy to tension and suspense.