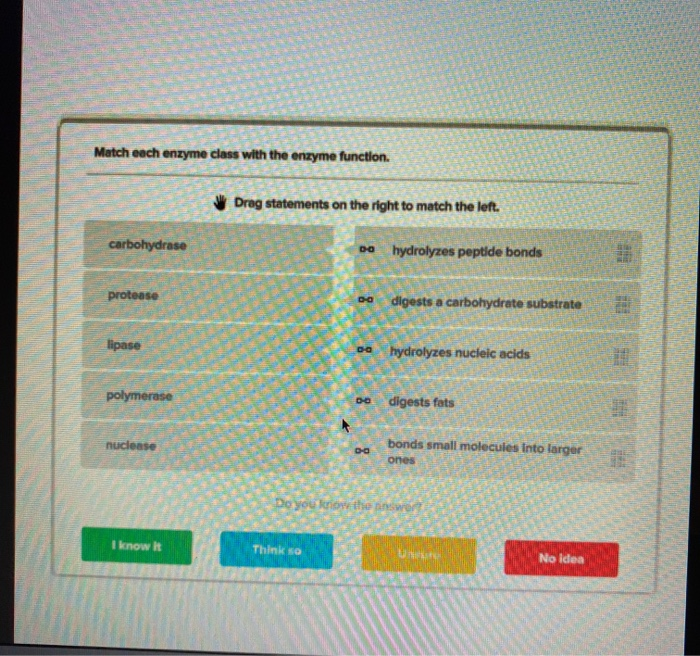
Match each enzyme class to the type of reactions catalyzed. – Embarking on an exploration of the intricate relationship between enzyme classes and the reactions they catalyze, this discourse unravels the complexities of this fundamental biochemical concept. Delving into the depths of enzyme classification, we uncover the criteria that govern the categorization of these molecular maestros, illuminating their diverse roles in orchestrating the symphony of life’s chemical transformations.
As we delve deeper, we unveil the myriad types of reactions catalyzed by enzymes, showcasing the remarkable versatility of these biological catalysts. From the hydrolysis of bonds to the intricate dance of redox reactions, enzymes orchestrate a vast repertoire of chemical transformations, underpinning the very fabric of cellular life.
Enzyme Classification
Enzyme classification is a systematic way of categorizing enzymes based on their structure, function, and mechanism of action. The International Union of Biochemistry and Molecular Biology (IUBMB) has established a comprehensive enzyme classification system that divides enzymes into six major classes:
- Oxidoreductases
- Transferases
- Hydrolases
- Lyases
- Isomerases
- Ligases
Each class is further divided into subclasses and sub-subclasses based on more specific criteria, such as the type of reaction catalyzed or the substrate specificity.
Types of Reactions Catalyzed by Enzymes

Enzymes catalyze a wide variety of chemical reactions, including:
- Oxidation-reduction reactions: These reactions involve the transfer of electrons between molecules.
- Transfer reactions: These reactions involve the transfer of a functional group from one molecule to another.
- Hydrolysis reactions: These reactions involve the cleavage of a bond between two atoms by the addition of water.
- Lysis reactions: These reactions involve the cleavage of a bond between two atoms without the addition of water.
- Isomerization reactions: These reactions involve the rearrangement of atoms within a molecule.
- Ligation reactions: These reactions involve the joining of two molecules together.
Matching Enzyme Classes to Reaction Types

| Enzyme Class | Type of Reaction Catalyzed |
|---|---|
| Oxidoreductases | Oxidation-reduction reactions |
| Transferases | Transfer reactions |
| Hydrolases | Hydrolysis reactions |
| Lyases | Lysis reactions |
| Isomerases | Isomerization reactions |
| Ligases | Ligation reactions |
Factors Affecting Enzyme Activity
The activity of enzymes is influenced by a number of factors, including:
- pH: Enzymes have an optimal pH range at which they are most active. Deviations from this optimal pH can lead to decreased enzyme activity.
- Temperature: Enzymes also have an optimal temperature range at which they are most active. Extreme temperatures can denature enzymes and lead to decreased activity.
- Substrate concentration: The rate of enzyme-catalyzed reactions is affected by the concentration of the substrate. At low substrate concentrations, the reaction rate is proportional to the substrate concentration. At high substrate concentrations, the reaction rate reaches a maximum velocity.
Applications of Enzyme Classification
Enzyme classification has a number of practical applications, including:
- Medicine: Enzyme classification is used to identify and characterize enzymes that are involved in disease processes. This information can be used to develop new drugs and treatments for diseases.
- Biotechnology: Enzyme classification is used to identify and characterize enzymes that can be used in industrial processes. These enzymes can be used to produce a variety of products, such as food, beverages, and pharmaceuticals.
- Environmental science: Enzyme classification is used to identify and characterize enzymes that are involved in environmental processes. This information can be used to develop new technologies for environmental remediation.
FAQ Guide: Match Each Enzyme Class To The Type Of Reactions Catalyzed.
What are the major criteria used to classify enzymes?
Enzymes are classified primarily based on the type of chemical reaction they catalyze, as well as the substrate specificity and cofactors they require.
How do enzymes affect the rate of chemical reactions?
Enzymes accelerate the rate of chemical reactions by lowering the activation energy required for the reaction to occur, enabling reactions to proceed more rapidly under physiological conditions.
What are some practical applications of enzyme classification?
Enzyme classification has numerous applications, including the development of enzyme inhibitors for therapeutic purposes, the design of enzymes for industrial processes, and the understanding of enzyme evolution and function in biological systems.